Sri Lanka: Learn More About Sinhalese
Sinhalese, or Sinhala as it is known locally in Sri Lanka, is potentially a surprising discovery to find on the Indo-European language family tree, since Indo-European tends to characterise the language group covering Europe, Iran, and North India. We all have that one family relative that sticks out like a sore thumb, but Sinhalese is more like the fabulous mad aunt we all wished we could be, instead of that surly, sulking cousin we're all glad we're not. Come take a look!
Photo via Wikimedia
Origins
Sinhalese is an old, old language. It's thought that the language was brought to Sri Lanka in the fifth or sixth century BCE, during the great Aryan immigration from Bengal led by Prince Vijaya of Singhapura. Linguists believe that Sinhalese derives from two probable sources; firstly, Sanskrit, much as Romance languages derived from Latin, and secondly, Prakit, of which the best representation may be found in Pali, the language of the Buddhist scriptures. Though Sanskrit is said to have contributed most, with much of modern Sinhalese vocabulary directly borrowing words from Sanskrit, such as prema (love), bhasha (language), and viplava (revolution).
Relationships
If we've already said Sinhalese is Indo-European, then it's no surprise there's a relationship between it and other languages within the same family. Romance languages, whose roots are in Latin, find their connection with Sinhalese because of the shared characteristics of Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, hailing from a common language ancestor.
Germanic languages also show similarities to Sinhalese, though they are harder to spot because of phonemic changes in the languages. Over time, these are the changes Germanic languages have seen:
bh — bdh — dgh — gp — ft — thk — h
Which reveals more similarities between the languages than you might think:
Susceptible to change
Sinhalese, because of its location, has long been susceptible to the influence of foreign linguistics, resulting in changes in the language or assimilation of loan words. Because of its proximity to South India, for example, Sinhalese comes into regular contact with the Dravidian language Tamil. The most influential period in terms of the assimilation of Tamil into Sinhalese was during an eleventh century invasion, which resulted in loan words such as padi (wages), sellam (play), and salli (money) becoming part of the Sinhalese everyday language.

Photo via Pixabay
Learning a new language? Check out our free placement test to see how your level measures up!
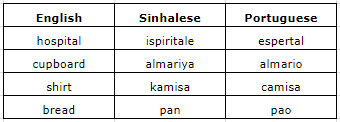
And while we're on the subject of change, we should recognise the effect of colonisation on Sinhalese, with the influence of Portuguese, Dutch, and English on the language during the sixteenth century. Portuguese shows the most notable influence:
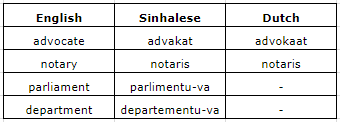
Though there are visible examples of both Dutch and English in everyday life:
Back to basics
Sinhalese is spoken by around 16 million people, with four million choosing it as their second language. It resides on the Southern Zone branch of the Indo-European family tree, and is the official language of Sri Lanka. Sinhalese has its own alphabet comprised of 23 consonants and 13 vowels, as well as its own form of braille. Its typology features a subject-object-verb sentence structure, postpositions, gendered nouns, an indefinite article suffix, and tenses.

Sigiriya via Pixabay
On the tip of your tongue
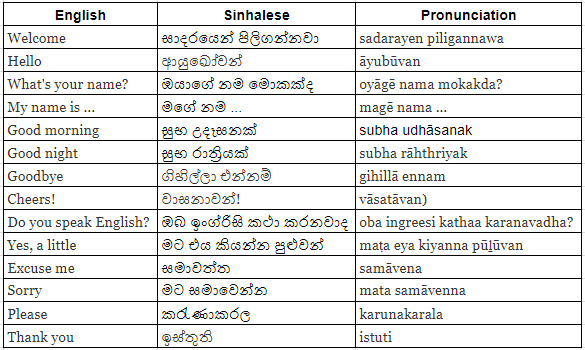
So here's a little Sinhalese for you to try yourself!
Isn't the Sinhalese alphabet beautiful?! And if that's not inspiration enough to want to learn this incredible language, well, we're not sure what will entice you in!